Image Credit & Copyright: Gerald Rhemann
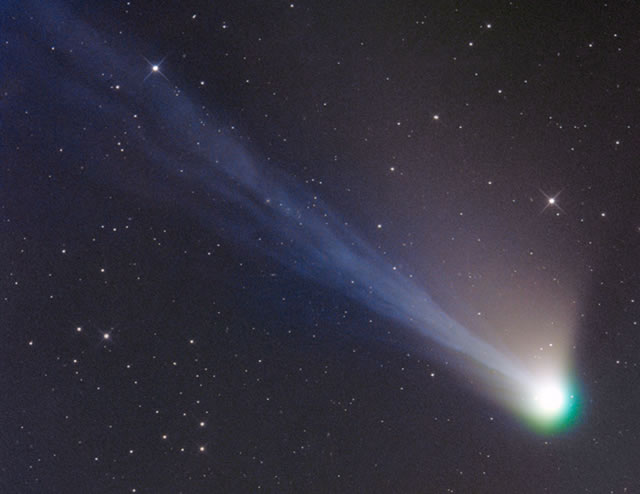
Cosa ha causato l’interessante e bellissima coda intrecciata che la Cometa Lemmon mostra dall’inizio di quest’anno? Prima di tutto, quasi ogni cometa che si avvicina al Sole mostra due code: una coda di polveri e una coda di ioni.
La coda di polveri della cometa Lemmon, visibile sopra e intorno al nucleo della cometa in bianco sporco, è prodotta dalla luce del sole che riflette la polvere che si sparge dal nucleo riscaldato della cometa. Fluente e più scolpita, tuttavia, è la nostra Cometa in osservazione, C/2012 F6 (Lemmon) che mostra una lunga coda blu di ioni, creata dal vento solare che spinge gli ioni espulsi dal nucleo distante dal sole. Degna di nota è il coma che circonda il nucleo della Cometa Lemmon, colorata di verde del gas di carbonio atomico fluorescente grazie alla luce del sole. L’immagine sopra è stata ripresa dai cieli bui della Namibia a metà aprile. La Cometa Lemmon sta ora svanendo mentre si dirige verso il sistema solare esterno.
What caused the interestingly intricate tails that Comet Lemmon displayed earlier this year? First of all, just about every comet that nears the Sun displays two tails: a dust tail and an ion tail.
Comet Lemmon’s dust tail, visible above and around the comet nucleus in off-white, is produced by sun-light reflecting dust shed by the comet’s heated nucleus. Flowing and more sculptured, however, is C/2012 F6 (Lemmon)’s blue ion tail, created by the solar wind pushing ions expelled by the nucleus away from the Sun. Also of note is the coma seen surrounding Comet Lemmon’s nucleus, tinted green by atomic carbon gas fluorescing in sunlight. The above image was taken from the dark skies of Namibia in mid-April. Comet Lemmon is fading as it now heads back to the outer Solar System.
Source/Continue reading → Apod.NASA.com