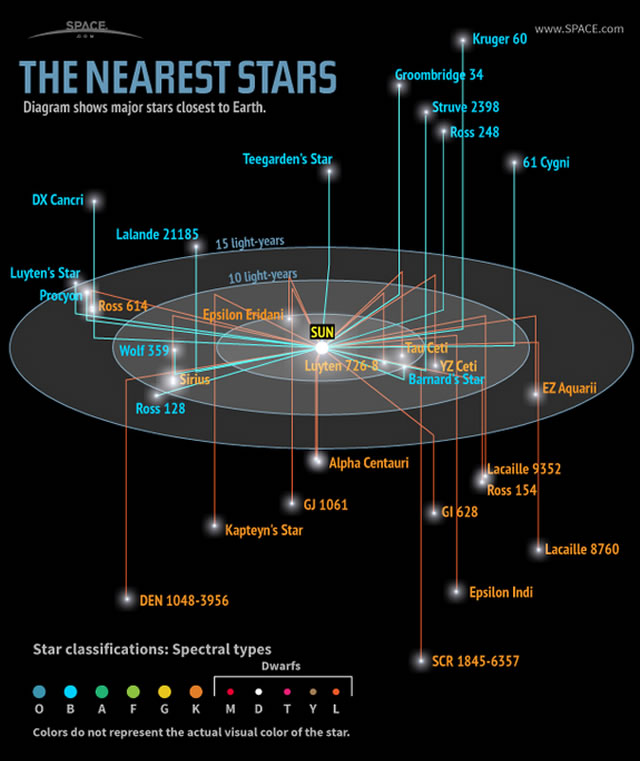
Le stelle più vicine alla Terra sono nel triplo sistema stellare di Alpha Centauri, a circa 4,37 anni luce di distanza.
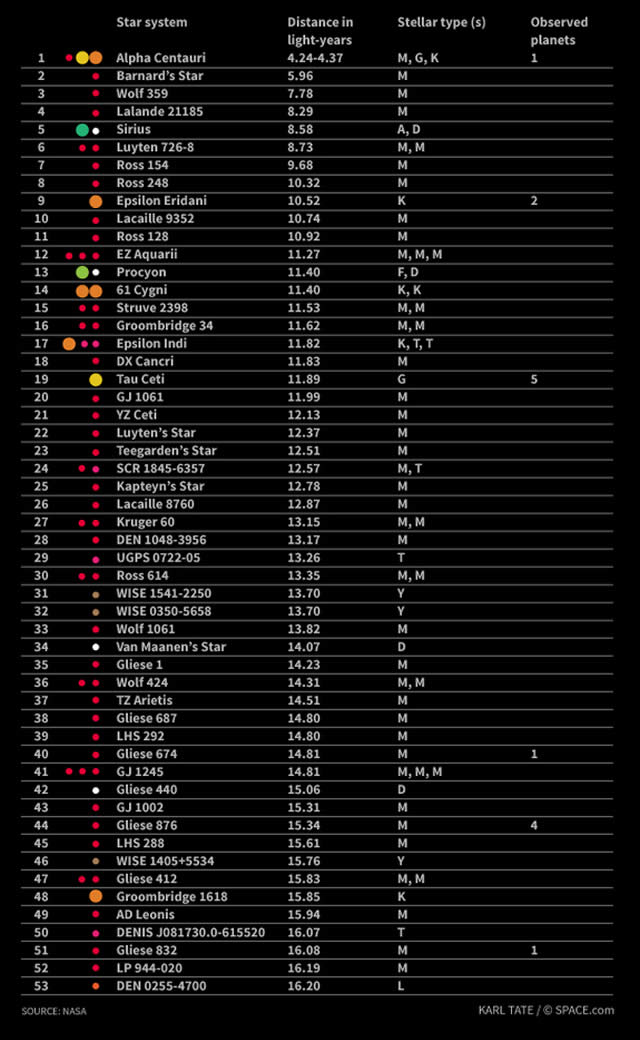
Una di queste stelle, Proxima Centauri, è leggermente più vicina, a 4,24 anni luce. Di tutte le stelle più vicine di 15 anni luce, solo due sono tipo spettrale G, simile al nostro sole: Alpha Centauri A e Tau Ceti. La maggior parte sono stelle nane rosse, di tipo M. Solo nove delle stelle in questa zona sono abbastanza brillanti da poter essere viste ad occhio nudo dalla Terra. Le stelle più luminose sono Alfa Centauri A e B, Sirio A, Epsilon Eridani, Procione, 61 Cygni A e B (61 Cygni – 61 Cyg, talvolta chiamata la Stella di Bessel o la Stella Volante di Piazzi, è una stella binaria visibile nella costellazione del Cigno. Consiste di una coppia di stelle arancioni di sequenza principale un po’ più piccole del Sole, che orbitano attorno al comune centro di massa in circa 659 anni. Di magnitudine 5 e 6, le componenti di 61 Cyg sono tra le stelle più deboli visibili ad occhio nudo senza alcuno strumento ottico), Epsilon Indi A e Tau Ceti. La stella di Barnard , una nana rossa che si trova a 5,96 anni luce di distanza, ha il più grande moto proprio di ogni stella conosciuta. Ciò significa che la stella di Barnard si sposta rapidamente sullo sfondo delle stelle più lontane, ad una velocità di 10,3 secondi d’arco per anno terrestre. Sirio A è la stella più luminosa nel cielo notturno della Terra, grazie alla sua luminosità intrinseca e la sua vicinanza a noi. Sirio B, una nana bianca, è più piccola della Terra, ma ha una massa pari al 98 per cento di quella del nostro sole. Alla fine del 2012, gli astronomi hanno scoperto che Tau Ceti può ospitare cinque pianeti di cui uno nella zona abitabile della stella. Tau Ceti è la stella singola di tipo G più simile al nostro sole (anche se il triplo sistema stellare di Alpha Centauri ospita anch’esso una stella di tipo G molto più vicina a noi).
The nearest stars to Earth are in the Alpha Centauri triple-star system, about 4.37 light-years away.
One of these stars, Proxima Centauri, is slightly closer, at 4.24 light-years. Of all the stars closer than 15 light-years, only two are spectral type G, similar to our sun: Alpha Centauri A and Tau Ceti. The majority are M-type red dwarf stars.Only nine of the stars in this area are bright enough to be seen by the naked human eye from Earth. These brightest stars include Alpha Centauri A and B, Sirius A, Epsilon Eridani, Procyon, 61 Cygni A and B (61 Cygni, sometimes called Bessel’s Star or Piazzi’s Flying Star, is a binary star system in the constellation Cygnus. It consists of a pair of K-type dwarf stars that orbit each other in a period of about 659 years, forming a visual binary. At fifth and sixth apparent magnitudes, they are among the least conspicuous stars visible in the night sky to an observer without an optical instrument), Epsilon Indi A and Tau Ceti. Barnard’s Star, a red dwarf 5.96 light-years away, has the largest proper motion of any known star. This means that Barnard’s Star moves rapidly against the background of more distant stars, at a rate of 10.3 seconds of arc per Earth year. Sirius A is the brightest star in Earth’s night sky, due to its intrinsic brightness and its proximity to us. Sirius B, a white dwarf star, is smaller than Earth but has a mass 98 percent that of our sun. In late 2012, astronomers discovered that Tau Ceti may host five planets including one within the star’s habitable zone. Tau Ceti is the nearest single G-type star like our sun (although the Alpha Centauri triple-star system also hosts a G-type star and is much closer).
Credit: SPACE.com





















Pingback: Caccia al Pianeta Alieno più vicino grazie a Raro Allineamento Stellare – Hunt for Closest Alien Planet Gets Rare Boost From Stellar Alignment | DENEB Official ©