Utilizzando i dati provenienti da un vecchio veicolo spaziale della NASA, i ricercatori hanno trovato i segni di una fonte d’energia del vento solare che ha catturato l’attenzione dei ricercatori.
La NASA sarà in grado di verificare la teoria entro questo decennio, quando verrà inviata una nuova sonda verso il Sole per osservazioni più ravvicinate. La scoperta è stata fatta da un gruppo di astronomi che cercano di risolvere un mistero vecchio di decenni: Cosa riscalda e accelera il vento solare? Il vento solare è un flusso caldo e veloce di gas magnetizzato che si sprigiona dalla atmosfera del sole. È fatto di idrogeno e ioni di elio, con pochi altri elementi più pesanti. I ricercatori lo paragonano al vapore di una pentola di acqua bollente su un fornello, come se il Sole stesso bollendo, evaporasse via. “Ma”, dice Adam Szabo del Goddard Space Flight Center della NASA, “il vento solare non è come il vapore che può essere creato nella vostra cucina. Come il vapore si alza da una pentola, rallenta e si raffredda. Invece, come il vento solare lascia il Sole, accelera, e si triplica in termini di velocità, passando attraverso la corona. Inoltre, qualcosa dentro al vento solare stesso continua ad aggiungere calore che soffia nel freddo dello spazio. “
Vento Solare
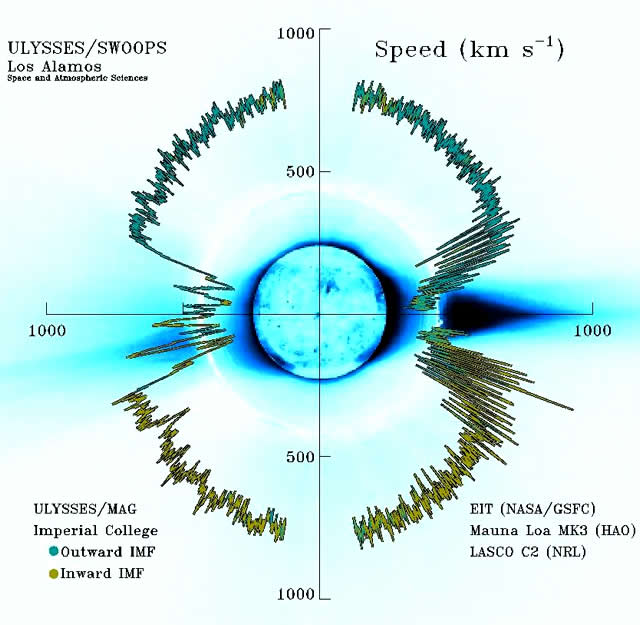
I flussi di vento solare si estendono dal Sole, in tutte le direzioni, ad una velocità di circa 400 km/s (circa 1 milione di miglia all’ora).
L’origine del vento solare è la calda corona della nostra stella. La temperatura della corona è così alta che la stessa gravità solare non può trattenerla. Anche se si capisce il perché di questo meccanismo, non si è ancora arrivati ad interpretare i dettagli su come e dove i gas coronali accelerano a queste alte velocità. Il quesito è legato alla questione del riscaldamento della stessa corona.
Variazioni del vento solare
Il vento solare non è uniforme. Anche se è sempre diretto lontano dal Sole, cambia velocità e porta con sé nubi magnetiche, interagendo con zone solari in cui la velocità più alta del vento raggiunge il flusso a bassa velocità, variandone la composizione. La velocità del vento solare è elevata (800 km/s) sui buchi coronali e bassa (300 km/s) sui filamenti. Questi flussi ad alta e bassa velocità interagiscono tra loro e interessano alternativamente la Terra con la rotazione del Sole. Il vento solare, con le sue variazioni di velocità, soffia sul campo magnetico della Terra e può produrre tempeste nella magnetosfera del nostro Pianeta.
Using data from an aging NASA spacecraft, researchers have found signs of an energy source in the solar wind that has caught the attention of fusion researchers.
NASA will be able to test the theory later this decade when it sends a new probe into the sun for a closer look. The discovery was made by a group of astronomers trying to solve a decades-old mystery: What heats and accelerates the solar wind? The solar wind is a hot and fast flow of magnetized gas that streams away from the sun’s upper atmosphere. It is made of hydrogen and helium ions with a sprinkling of heavier elements. Researchers liken it to the steam from a pot of water boiling on a stove; the sun is literally boiling itself away. “But,” says Adam Szabo of the NASA Goddard Space Flight Center, “solar wind does something that steam in your kitchen never does. As steam rises from a pot, it slows and cools. As solar wind leaves the sun, it accelerates, tripling in speed as it passes through the corona. Furthermore, something inside the solar wind continues to add heat even as it blows into the cold of space.”
Source/Continue reading → NASA.gov
Solar Wind
The solar wind streams off of the Sun in all directions at speeds of about 400 km/s (about 1 million miles per hour).
The source of the solar wind is the Sun’s hot corona. The temperature of the corona is so high that the Sun’s gravity cannot hold on to it. Although we understand why this happens we do not understand the details about how and where the coronal gases are accelerated to these high velocities. This question is related to the question of coronal heating.
Solar Wind Variations
The solar wind is not uniform. Although it is always directed away from the Sun, it changes speed and carries with it magnetic clouds, interacting regions where high speed wind catches up with slow speed wind, and composition variations. The solar wind speed is high (800 km/s) over coronal holes and low (300 km/s) over streamers. These high and low speed streams interact with each other and alternately pass by the Earth as the Sun rotates. These wind speed variations buffet the Earth’s magnetic field and can produce storms in the Earth’s magnetosphere.
Source/Continue reading → NASA.gov