Stonehenge – Solstizio d’Estate – Summer Solstice
Il solstizio in astronomia è definito come il momento in cui il Sole raggiunge, nel suo moto apparente lungo l’eclittica, il punto di declinazione massima o minima.
Il fenomeno è dovuto alla inclinazione dell’asse di rotazione terrestre rispetto all’eclittica; il valore di declinazione raggiunta coincide con l’angolo di inclinazione terrestre e varia con un periodo di 41000 anni tra 22.1° e 24.5°. Attualmente è di 23°27′ e l’angolo è in diminuzione. Il Sole raggiunge il valore massimo di declinazione positiva nel mese di giugno in occasione del solstizio di estate boreale, mentre raggiunge il massimo valore di declinazione negativa in dicembre, in occasione del solstizio di inverno boreale, corrispondente all’estate nell’emisfero australe. Da un esame di una tabella dei tempi dei solstizi si può verificare che il fenomeno ritarda di circa sei ore ogni anno (5 ore, 48 minuti e 46 secondi per la precisione), salvo subire un nuovo riposizionamento indietro ogni quattro anni, in conseguenza degli anni bisestili, introdotti proprio per evitare un progressivo disallineamento delle stagioni con il calendario. A causa di queste variazioni può capitare che il solstizio astronomico cada nell’emisfero nord (emisfero boreale) il 20 o il 21 giugno per l’estate, o il 21 o 22 dicembre per l’inverno. L’evento è interpretato e festeggiato da diverse culture in tutto il mondo.
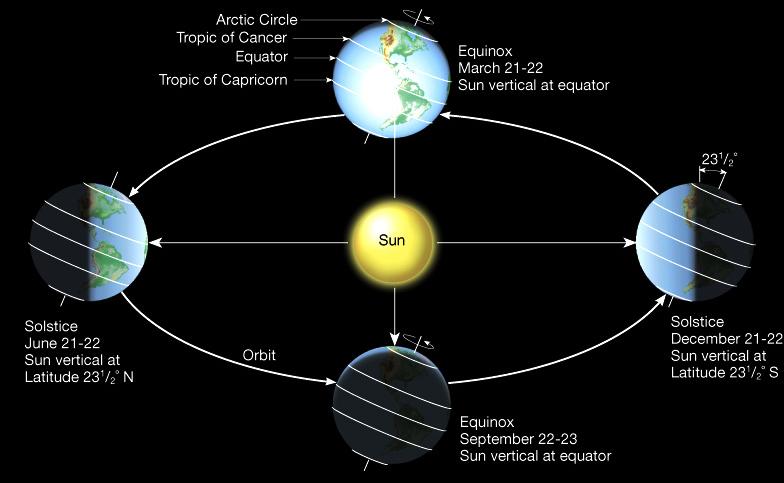
Solstice and Equinox – Solstizio ed Equinozio
The summer solstice occurs when the tilt of a planet’s semi-axis, in either the northern or the southern hemisphere, is most inclined toward the star (sun) that it orbits.
Earth’s maximum axial tilt toward the sun is 23° 26′. This happens twice each year, at which times the sun reaches its highest position in the sky as seen from the north or the south pole. The summer solstice occurs during a hemisphere’s summer. This is northern solstice in the northern hemisphere and the southern solstice in the southern hemisphere. Depending on the shift of the calendar, the summer solstice occurs some time between December 20 and December 23 each year in the southern hemisphere and between June 20 and June 22 in the northern hemisphere in reference to UTC. Though the summer solstice is an instant in time, the term is also colloquially used like midsummer to refer to the day on which it occurs. The summer solstice occurs on the day that has the longest period of daylight – except in the polar regions, where daylight is continuous, from a few days to six months around the summer solstice. Worldwide, interpretation of the event has varied among cultures, but most recognize the event in some way with holidays, festivals, and rituals around that time with themes of religion or fertility.
Source/Continue reading → Wikipedia